Flying Brave Bird 2 Flappy Again With Tiny Wings Sensor Tower
The Roles of Take a chance and Luck in Innovation
One of the most controversial, and maybe even misunderstood topics in innovation are the roles of risk and luck for innovation success. Do yous have to go lucky to innovate successfully, or can you make your own luck? Is it always inherently risky to endeavour to innovate, or can you manage adventure by making smart decisions? These are fundamental questions I'thou sure every innovator has had to battle with throughout their journey, but that don't unremarkably get the attention they deserve. And so, in this commodity, I'll be sharing my thoughts on how these matters affect innovation, and what you can do to improve your odds of success. Before nosotros tin can dive into the practicalities, information technology's important nosotros first sympathize what risk really means since at that place's quite a bit of debate virtually the nuances of the term. Is risk always negative, or tin can information technology also be positive? What is the departure between hazard and uncertainty? For example, in academia, take a chance typically only refers to situations where the probabilities of the outcome are known in advance, such as most gambling situations, but non to situations where the probability distribution is unknown, such equally business and innovation. These are import considerations to sympathize, but for our context of innovation, risk is very much synonymous with incertitude, and can simply be considered to refer to all kinds of situations where the outcome isn't known in accelerate. Circling back to chance and innovation, allow'due south expect at what risk means for innovators, or in other words, people that are trying to introduce something new (anything from products and services to process improvements) to the market. The of import thing to sympathise here is that as innovators are, by definition, working on something new, there are always many more than unknowns in the process than there is in doing business equally usual. For example: This means that there's much more run a risk in doing innovation, than there is in doing business equally usual. However, as nosotros learned earlier, risk isn't necessarily merely a bad thing. Taking risk in an uncertain environment tin besides lead to better-than-expected outcomes. Taking gamble in an uncertain environment can lead to better-than-expected outcomes, and without innovation, y'all have a 100% probability of going out of business. Nigh leaders obviously know this, but in real life things are rarely that black and white. Usually the real question is about how to take smart, educated risks in a given situation. In practice, this leads to questions such as: how aggressively to invest, with what timelines and resource, are y'all willing to cannibalize your existing business or only invest in expanding to new business organisation areas etc. Even so, where we see a lot of managers and leaders get into trouble is when they think they tin brand decisions related to the innovation the same style they can for incremental improvement of existing businesses. For example: When you're considering the risks of increasing production line chapters for an existing business organization, the expected benefits, costs and risks related to the project are ordinarily pretty straightforward to assess and calculate, which means that it's easy to make a very educated, data-driven decision. I'd like to highlight that this doesn't mean that yous should make uninformed decisions, information technology just means that you have to accept that you tin can't know everything earlier yous make a conclusion, and will thus likely demand to adapt grade at some point after that initial determination. For those new to innovation, this shift in mindset will be crucial for your ability to succeed. So, allow'due south take a stride back and consider the typical outcomes an innovator might expect to run into with their innovation efforts. In full general, there are 5 typical outcomes: Furthermore, the probability of you landing on any ane of these outcomes will always vary significantly based on a number of things, such as your industry, appetite level, your capabilities, the competition, and many other dynamic circumstances in the market that could be attributed to luck. As nosotros've established, with a topic that has as many unknowns as innovation, luck clearly plays a office in all of this. The big, age-sometime question that we always hear beingness debated is: can you lot make your own luck, or is that something that is out of your control? There are many vocal proponents and expert arguments for each side of the argument. Yet, equally this isn't a black and white topic, it'southward probably easiest to explain with an example from a completely dissimilar field. Let's say that a young boy wants to become a top basketball player and accept a career in the NBA. Will they exist able to go far if they just railroad train incredibly hard and smart ever since they were 5 years quondam? Probably non if they end up simply being v anxiety tall equally an developed. Likewise, if that boy is being born in, let'south say rural Africa, they probably won't have the same opportunities to even play the sport, let alone have equally capable coaches and opponents to play against than someone born in a big urban center in the U.s.a.. And so, genes and the environment, both of which are largely owing to luck, and that are essentially out of your control, definitely play a meaning role here. However, let's look at the other side of the story. Would Michael Hashemite kingdom of jordan take become the star he was without being as determined and competitive, equally well equally putting in thousands and thousands of hours of dedicated do? And the reply is without a doubtfulness: no. So, to really succeed at the highest levels of anything, you lot ever have to piece of work both difficult and smart, likewise as likewise have luck on your side. If you lot're just determined enough and willing to put in the work, and y'all do that in a smart, systematic way, I really think most people and companies have the prerequisites to become very proficient at a number of things, including business and innovation – even if the average company probably won't become the next Apple or Microsoft. So, in the end, you still can't entirely make your own luck, but y'all can dramatically improve the odds of luck being on your side – and get pretty good results fifty-fifty without that stroke of luck. Here's a unproblematic matrix that can hopefully illustrate the role of luck in innovation success: On the other paw, if you don't take any of the skills and capabilities needed to introduce – and aren't working on anything that could lead to bigger successes downwards the road, you don't actually stand up a chance. And in a lot of cases betwixt these two extremes, luck can often brand the departure between failure and success, but that doesn't mean that you shouldn't effort to rig the game to your advantage. So, with that in heed, there are still plenty of things you can practice to minimize risk, eliminate some of the unknowns in innovation, and significantly improve your odds of somewhen succeeding. Let's look at some of the key ways in which you can accomplish the these goals. This is by no means a complete list, but more of an overview of some of the more of import matters. The first slice of communication is to focus on the affair that customers really need done, non on superficial qualities such as production features or fifty-fifty the competitive landscape. This is what the Jobs-to-exist-washed theory is all about. On many occasions, specially in consumer-facing businesses, but also in B2B, there's seemingly a lot of information about the customer, who they are, what they do, and so forth, but all too oft we forget the near important office: what they really need your production or innovation for. The difference is subtle only can make all the difference in the globe for what you really offer to your customers, and how you lot market and sell it to them. Here's Clayton Christensen explaining how this works with the classic example of a milkshake: As it turns out, if y'all just get the "chore" right, you volition dramatically decrease the probability of yous running out of money to build your product equally you can focus on edifice merely what the customer needs – and not everything possible nether the sun – or the product failing to create value enough value. Getting the "job" correct usually helps unlock demand from new parts of the market where there's little competition. And as was the instance in Christensen's example, you might fifty-fifty find that your market place is many times larger than you initially thought. If you've been post-obit our blog for some time, you might remember my piece on the stride of innovation existence the ultimate competitive advantage. I notwithstanding stand by that claim, and it'due south also a great tool for reducing the role of luck and managing risk in innovation. As a quick recap, pace of innovation merely ways the rate at which you introduce innovations, or in other words, novel changes, to your business organization or towards your customers. The faster you are, the more likely you lot obviously are to be ahead of your competitors, merely that isn't fifty-fifty the cardinal benefit here. The existent benefit comes from yous focusing on action instead of planning. In near medium and large organizations, there's usually a bias towards the latter, often for very logical reasons, but when you're working on something with a lot of unknowns, the unfortunate truth is that the plans aren't going to be very useful most of the fourth dimension. So, the faster you tin make your ideas happen and see how they work in real life, the faster y'all'll larn which parts piece of work well, and which don't, and the faster you can amend upon the beginning version, which rarely is an instant success. If yous're having problem accelerating your stride of innovation, or in making things happen in general, information technology's quite probable that either: If you're familiar with the Lean Startup model, agile methods, or literally almost any of the other modernistic innovation processes and frameworks, that's what they besides effort to aid you lot do. Just, if you lot break that big project down into very pocket-sized chunks that can exist completed in days or weeks, you accept no option merely to get things done, and once that happens, your pace of innovation inevitably accelerates and every time you become something out in the market, no matter how small, you can eliminate a small part of the uncertainty involved that innovation. Even if the improvement itself doesn't prove useful, at least you know that for a fact and tin can focus on something else – instead of spending time and resources on perfecting that thing. Every fourth dimension you get something to the market, no matter how small, you can eliminate a small role of the incertitude involved in that innovation What's more, one time you lot've cleaved those big scary innovations into smaller, much more manageable chunks, you'll be pleasantly surprised to run into that in most cases, there will be plenty of more mundane assignments that your team volition be more than than capable of successfully executing, even if they aren't exactly known as innovation all-starts. 4. Systematize innovation, don't just leave it for the few Finally, as long as innovation is something that simply a few people, or a single team, within your arrangement are working on, and you don't have a systematic process towards managing it, you really are leaving innovation up to hazard. However, if you systematize innovation, and engage as many people as possible to exercise their part in progressing your innovation calendar, you can dramatically improve your odds of making more innovation happen. It's a simple law of probabilities: a few people tin only work on a few ideas, whereas thousands of people can work on hundreds or thousands of them. So, as innovation involves a lot of uncertainty, you volition dramatically improve your odds by just increasing your chapters to evangelize innovation to market even with dumb luck. And if you closely observe the affect of these smaller innovations, y'all can farther focus your resources towards areas that seem to accept potential for moving the needle, further improving your odds of getting innovation right. Let's recap: to innovate, you have to exercise what others haven't however done, and to do that, you have to think differently and accept some take chances. To introduce, you take to practice what others oasis't yet washed, and to do that, you have to retrieve differently and have some risk – just also try to rig the game to your advantage. In other words, innovation is always risky, and luck always plays a function in it, but if y'all play your cards right, yous will do extremely well in the long run. If you're interested in a applied plan that walks you through the entire process, y'all might be interested in our Innovation System, and if you're looking to stay upwardly to date on everything innovation, subscribe to our blog!
What does chance mean?  So, for our purposes, let's just think of take a chance as situations where we can't know the consequence of a decision or action in advance. So, more things could happen than will happen.
So, for our purposes, let's just think of take a chance as situations where we can't know the consequence of a decision or action in advance. So, more things could happen than will happen.
Risk and innovation
On the other paw, if you don't take risk and introduce, the competition volition always somewhen surpass you, which means that without investing in innovation, you have a 100% probability of going out of business organization.
Innovation requires a more qualitative approach to risk On the other hand, if you're looking for new growth opportunities with innovation, it'southward important to empathize that no matter what kind of studies you committee, they might help you empathise the playing field better, simply you'll still need to make decisions based on more than qualitative data, and with more unknowns, which many leaders in large organizations are very uncomfortable with.
On the other hand, if you're looking for new growth opportunities with innovation, it'southward important to empathize that no matter what kind of studies you committee, they might help you empathise the playing field better, simply you'll still need to make decisions based on more than qualitative data, and with more unknowns, which many leaders in large organizations are very uncomfortable with.
Typical outcomes for innovators
Equally we've already discussed, while you tin can try to estimate your odds of ending up in each of these scenarios beforehand, it actually isn't possible to know what the exact probability distribution of the scenarios really is similar. Still, it is of import to understand what the possible outcomes might be, so that you know what to expect on the journey and can prepare appropriately – fifty-fifty if you don't have all the answers, or heck, even all the questions.
Still, it is of import to understand what the possible outcomes might be, so that you know what to expect on the journey and can prepare appropriately – fifty-fifty if you don't have all the answers, or heck, even all the questions.
The office of luck in innovation  And so, to really succeed at the highest levels of anything, you ever have to piece of work both hard and smart, every bit well equally also have luck on your side.
And so, to really succeed at the highest levels of anything, you ever have to piece of work both hard and smart, every bit well equally also have luck on your side.
Nonetheless, I do believe that as the Internet and globalization have democratized access to data and dramatically driven downwards the prices in many fields, the function of luck is now smaller than it has ever been.
On 1 hand, y'all have to be at the right time in the right identify, have all the needed skills and capabilities, practise everything right, and even then, get a flake lucky to get to those incredible quantum success stories nosotros often hear about.
Improving your odds
ane. Focus on the jobs that customers demand done
ii. Increase your pace of innovation 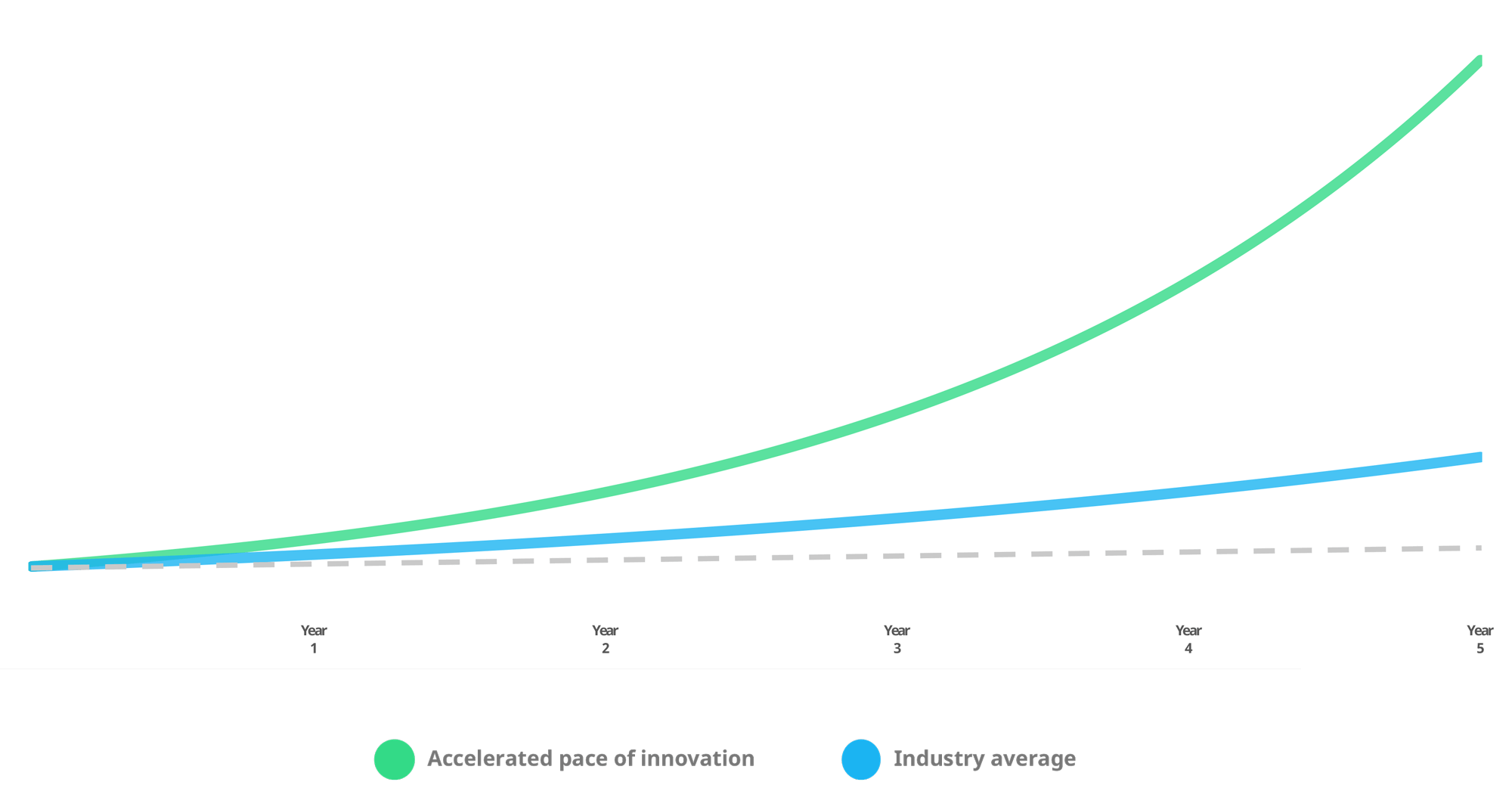
3. Intermission your plan down into small chunks to make information technology actionable
Well, the cure for either of these, and many other innovation challenges, is to intermission your plan down into smaller chunks to make things more actionable.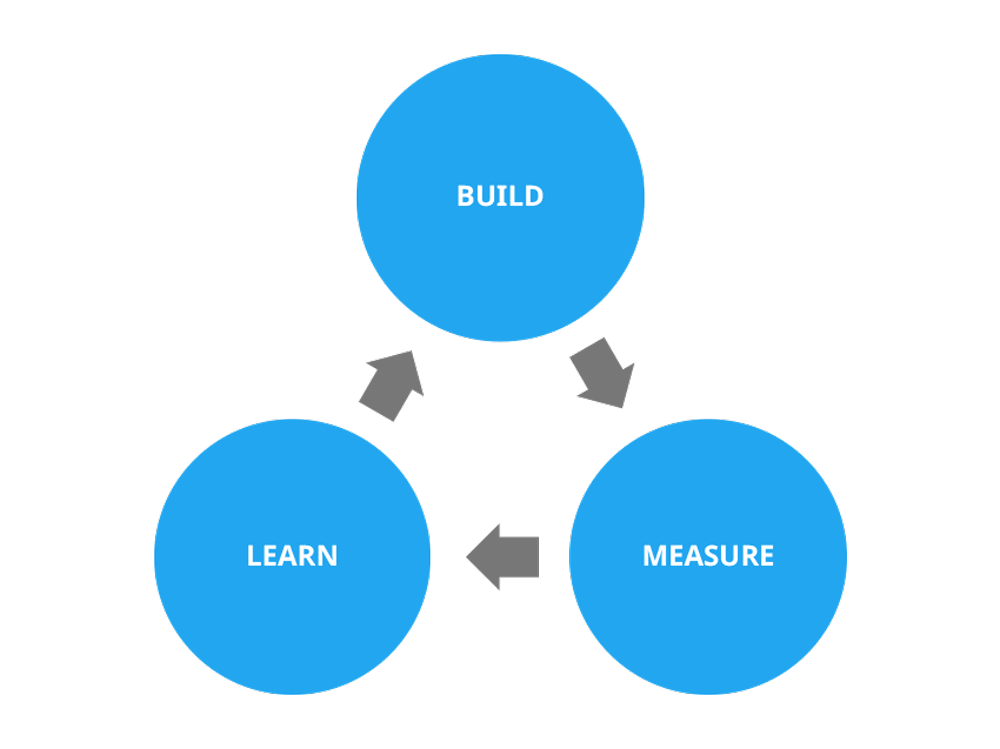 Creating a new innovation is usually quite an aggressive, scary and overwhelming task, so particularly if you're new to it, there'due south often a tendency towards staying in your comfort zone. For most people working on innovation, that is within the cozy walls of your role (or these days home), instead of really getting your easily dirty and committing to deliver real, tangible value towards your customers as presently equally possible.
Creating a new innovation is usually quite an aggressive, scary and overwhelming task, so particularly if you're new to it, there'due south often a tendency towards staying in your comfort zone. For most people working on innovation, that is within the cozy walls of your role (or these days home), instead of really getting your easily dirty and committing to deliver real, tangible value towards your customers as presently equally possible.
Conclusion
Still, you should try to rig the game to your advantage and try to brand the about out of the manus luck has given you lot – merely besides to position yourself then that y'all might get lucky in the future by building the right capabilities, structures and working on opportunities with existent potential.
Source: https://www.viima.com/blog/risk-and-luck-in-innovation
0 Response to "Flying Brave Bird 2 Flappy Again With Tiny Wings Sensor Tower"
Post a Comment